A private cloud is a cloud computing environment where all the underlying computing resources, such as servers, storage, and network, are dedicated to a single organization. Due to this exclusivity and internal control, a private cloud is also referred to as an internal or corporate cloud.
Enterprises have accelerated private cloud adoption, attributed to its ability to host both traditional VM-based applications and modern containerized and AI workloads, alongside benefits such as agility, elasticity, scalability, security, data sovereignty and regulatory compliance, and customizable resource management akin to on-prem infrastructure.
United Private Cloud® is a leading example of a highly secure, scalable private cloud platform designed to support these enterprise demands with advanced software-defined infrastructure (SDI) and global reach.
A private cloud operates as a single-tenant environment, where all underlying cloud compute resources are dedicated to a single organization. This is typically referred to as isolated access. Private cloud infrastructure can be hosted within an organization’s own data center, deployed at a third-party colocation facility, or extended to edge computing locations.
Management models are flexible: enterprises may choose to operate and maintain the environment entirely in-house or outsource some—or all—management responsibilities to a service provider, depending on their resources and strategic priorities.
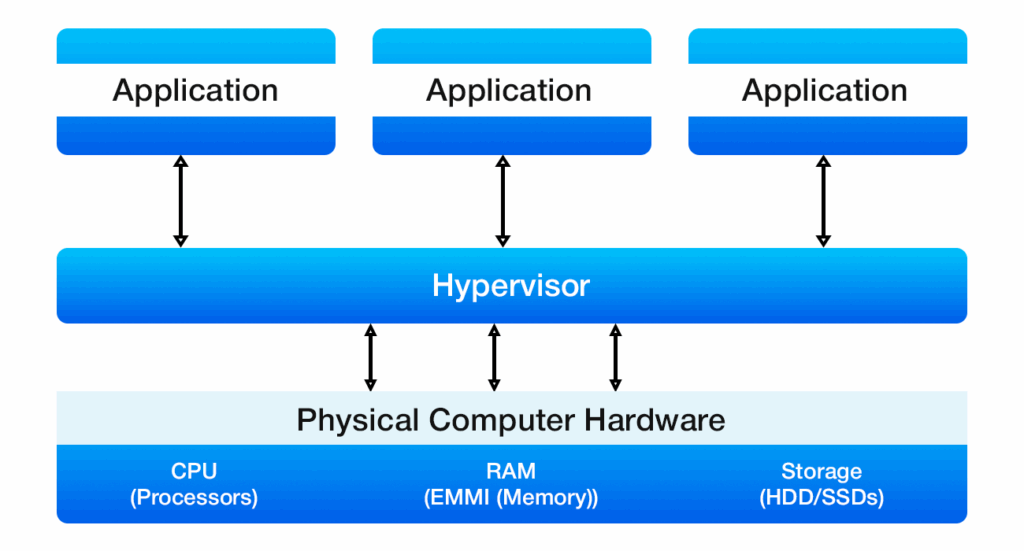
In addition, private clouds often use containerization—a lightweight form of virtualization that packages applications and their dependencies into portable containers for efficient deployment and scalability, often orchestrated by tools like Kubernetes.
Network virtualization abstracts and isolates physical network resources to create multiple autonomous virtual networks, enabling private clouds to segment, secure, and manage traffic independently of the underlying hardware. This underpins software-defined networking (SDN) and supports flexible network architectures such as VLANs, VXLANs, and micro-segmentation.
Additionally, private cloud networking incorporates network redundancy, high availability, load balancing, multi-layer security (with firewalls, intrusion detection), software-defined WAN (SD-WAN), and network function virtualization (NFV), and performance optimizations such as Remote Direct Memory Access (RDMA) and NVMe over Fabrics.
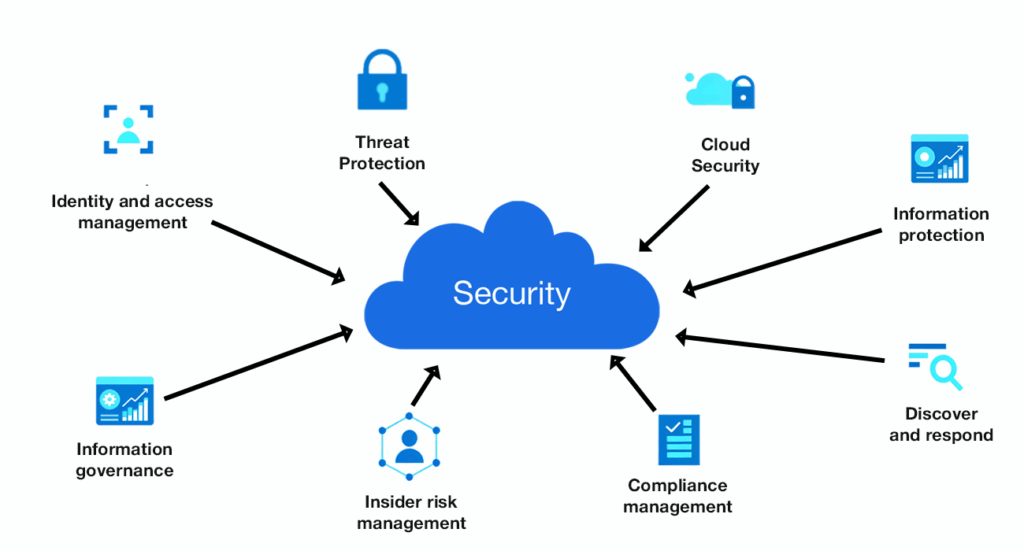
A cloud management platform provides administrators centralized control over private cloud infrastructure, multi-cloud, hybrid cloud environments, and the applications running within them. This enables optimization of cost, security, availability, resource utilization, compliance, and governance within the private cloud environment.
Cloud management platform (CMP) such as UnityOne.AI leverages AI-driven intelligence to simplify and automate cloud operations.
Automation technologies streamline complex operations by managing repetitive and error-prone tasks such as server provisioning, integrations, patch management, and scaling. Additionally, built-in Agentic AI takes automation further by autonomously handling complex cloud workflows, optimizing resource use in real time, and responding to dynamic demands across the environment.
In private cloud environments, organizations also adopt cloud-centric development and deployment practices such as DevOps, DevSecOps, microservices, and containerization to accelerate agility, security, and scalability.
Moving forward, it is important to understand that private cloud solutions come in four distinct types, each designed to meet different business needs and deployment requirements.
To address rising security demands, private clouds now incorporate confidential computing, safeguarding data even while it’s in use. By leveraging trusted execution environments (TEEs), enterprises can securely process sensitive workloads—such as financial transactions, healthcare records, or intellectual property—without risking exposure to unauthorized access.
While these emerging trends are shaping the future of private cloud computing, driving enterprise agility, security, and innovation in 2025 and beyond, they are also positioning private cloud as a strategic equivalent to public clouds, offering advantages such as robust security and compliance, flexibility and control, consistent performance and reliability, scalable resources, and long-term cost efficiency.
In addition, IT modernization, seamless integration with legacy systems, and the shift toward AI-first digital transformation remain key drivers for private cloud adoption.
However, to fully understand the value of a private cloud, it is essential to see how it differs from the public cloud model—a distinction that shapes decisions around resource control, security, scalability, and cost.
Public cloud operates on a multi-tenant foundation, where a third-party provider owns and manages large pools of computing resources shared among many customers. Users access these resources on a subscription or pay-per-use basis, much like a utility, benefiting from rapid elasticity and near-instant scalability without upfront hardware investment. This model offers low entry costs and economies of scale, enabling quick and cost-effective access to the latest technologies.
However, the shared nature of public cloud means organizations have less granular control over infrastructure and limited customization of security. In contrast, a private cloud is dedicated exclusively to a single organization, providing full authority over infrastructure, resource allocation, security policies, and compliance mandates such as data sovereignty. This ensures stable performance and tailored environments but often requires higher upfront investment and greater IT management expertise.
In short, public cloud excels in flexibility, cost efficiency, and rapid innovation—ideal for variable, less sensitive workloads. Private cloud is best suited for organizations that require maximum control, strict compliance, predictable performance, and specialized infrastructure to run modern AI and containerized workloads.
The emergence of hybrid cloud models further expands these options, blending the best of both approaches.
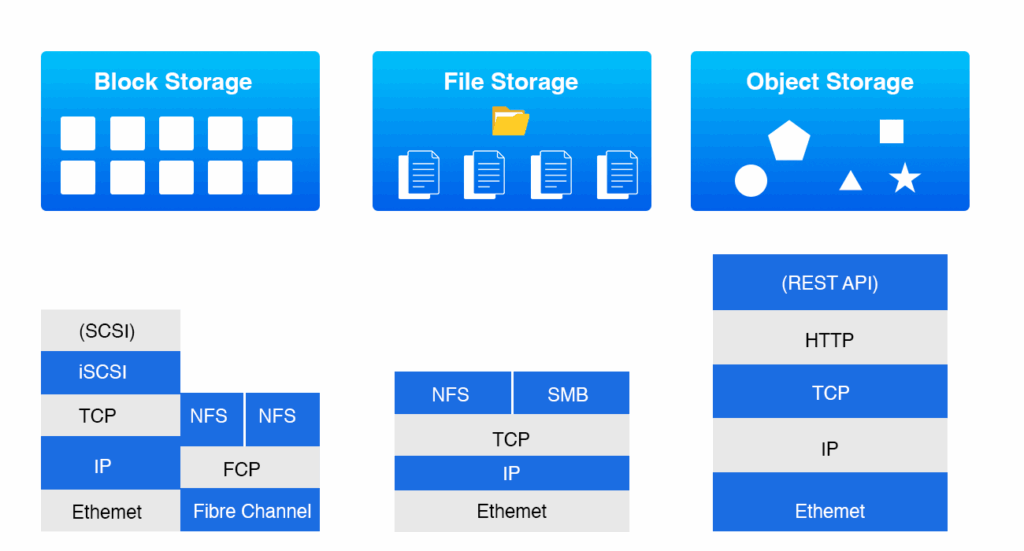
A private cloud provides exclusive control over dedicated infrastructure, including compute, storage, and network resources. Its architecture typically includes advanced hypervisors, multiple storage tiers (block, file, object), software-defined networking (SDN), identity and access management (IAM), encryption, firewalls, and centralized management platforms. This design is particularly suited for predictable, compliance-driven, and performance-sensitive workloads.
Hybrid cloud, on the other hand, integrates private and public cloud environments, combining the control and compliance of private infrastructure with the elasticity and scale of public providers. This integration is enabled through secure VPNs, dedicated interconnects, cloud management platforms, and orchestration frameworks that support seamless workload migration and unified visibility.
In a hybrid setup, sensitive workloads and regulated data remain within the secure boundaries of the private cloud, while burst workloads, testing, or innovation initiatives leverage the scalability of public cloud. Networking across the hybrid boundary uses SD-WAN and API-driven connectivity to enforce consistent security, governance, and performance SLAs.
While hybrid cloud delivers unmatched flexibility, it also introduces operational complexity in integration, policy enforcement, security consistency, and orchestration. This often requires advanced management tools and skilled governance to ensure workload portability, visibility, and compliance.
The distinction lies in operational agility: private cloud offers deep control and predictable performance, while hybrid cloud extends these advantages with the scalability, innovation capacity, and cost optimization of public cloud.
It’s this “best of both worlds” approach that explains the growing adoption of hybrid cloud—according to a recent Gartner survey, 81% of enterprises now work with multiple public cloud providers and hybrid management models.
With 25+ years of expertise in designing, deploying, and managing mission-critical IT environments for hundreds of organizations worldwide—from Fortune 500 enterprises to U.S. government agencies—UnitedLayer has established itself as a trusted leader in private and hybrid cloud solutions as well as managed data center hosting services.
UnitedLayer helps enterprises reduce costs, increase agility, and accelerate innovation, all while retaining the security, compliance, and control of a private cloud environment through its flagship United Private Cloud®.
UnitedLayer recognized as a “Leader” in the Private/Hybrid Cloud – Data Centre Services 2025 by ISG
United Private Cloud® is UnitedLayer’s proprietary, software-defined private cloud platform, delivering 100+ IaaS services from Tier 3+ data centers in 30+ private cloud regions and 175+ edge locations across five continents.
It enables enterprises to run modern workloads, including AI, machine learning, and containerized applications, with 99.999% high-availability, built‑in disaster recovery, and intelligent cloud management. Beyond secure application hosting, it guarantees data sovereignty and end‑to‑end regulatory compliance.
In addition, UnitedLayer offers an integrated ecosystem of advanced solutions that elevates the power of United Private Cloud®. UnitedEdge® delivers low-latency, high-availability edge computing, UnitedConnect® provides secure interconnection with major hyperscalers for seamless hybrid integration, and UnitedSecure ensures AI-driven, multi-layered security with zero-trust protection and real-time threat intelligence.
United Private Cloud for AI Workloads is UnitedLayer’s AI innovation backbone, designed to accelerate and scale next-generation AI and machine learning applications. It provides an integrated workflow that supports Private LLM-as-a-Service, enabling seamless monitoring, configuration, orchestration, and a natural language interface for reasoning, automation, and remediation.
Built on GPU-accelerated compute, all-flash storage, and low-latency networking, this environment ensures high performance, data sovereignty, multi-cloud connectivity, and robust governance, empowering organizations to deploy AI/ML workloads, MLOps pipelines, and advanced models at scale while accelerating AI innovation.
A private cloud is a dedicated cloud computing environment where an organization has exclusive access to servers, storage, and networking, ensuring stronger security, compliance, and control compared to public clouds.






Copyright © 2025 • All Rights Reserved